Configuration file settings
The EPTlib application is configured by a .toml file.
Table of contents
In .toml files, the symbol # marks the rest of the line as a comment, except when inside a string.
Title and annotations
title = "Example"
description = "Just an example of configuration file"
The title and the description will appear in the log of the EPTlib application.
Method
method = 0
The method is selected according to the following table.
| Code | Method |
|---|---|
| 0 | Helmholtz EPT |
| 1 | Convection-reaction EPT |
| 2 | Gradient EPT |
| 100 | Helmholtz EPT with automatically selected kernel |
Starting from the code 100, the implemented methods are still experimental.
Mesh
[mesh]
size = [128,128,8]
step = [1e-3,1e-3,4e-3] # [m]
sizeis the number of voxels of the input data in each direction.stepis the size of a voxel in meters.
Take care that Python h5py package stores the data in row-major order. If you are using Python h5py to create or inspect the input HDF5 datasets, the
sizeto be reported in the configuration file is the shape of the dataset ordered from the last to the first dimension. It can be obtained like reported in the tutorial, wherenn = tx_sens.shape size = nn[::-1]
Input
[input]
frequency = 64e6 # [Hz]
tx-channels = 2
rx-channels = 4
tx-sensitivity = "phantom.h5:/tx_sens>"
trx-phase = "phantom.h5:/trx_phase><" # [rad]
wrapped-phase = false
reference-image = "phantom.h5:/ref_img"
frequencyis the Larmor frequency of the input data in hertz.tx-channelsis the number of transmit channels in the input data.rx-channelsis the number of receive channels in the input data.tx-sensitivityis the address of the transmit (Tx) sensitivity (magnitude). It must be a dataset in an .h5 file.trx-phaseis the address in an .h5 file of the transceive (TRx) phase in radians. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. Alternatively, it is possible to provide the address of the transmit (Tx) phase in radians with the optiontx-phase. It is not possible to define bothtrx-phaseandtx-phasein the same configuration file.wrapped-phaseis equal totrueif the input transceive phase maps are wrapped. Currently, only the phase-based methods take advantage of it (default:false).reference-imageis the address in an .h5 file of a reference image that can be used by the EPT methods and the postprocessing. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. If it is an empty string, all the methods will be applied with no reference image (default: empty string).
For some EPT methods, the tx-sensitivity or the trx-phase (or tx-phase) could be optional.
In case of multiple transmit channels, the wildcard character > is used in the tx-sensitivity address in order to distinguish the data from each channel. It will be replaced by an increasing integer number from zero up to the number of transmit channels minus one.
Similarly, multiple receive channels are distinguished in the trx-phase (or tx-phase) address by means of the wildcard character <, which will be replaced by an increasing integer number from zero up to the number of receive channels minus one.
For example, with the previous input settings the transmit sensitivity data would be read from
"phantom.h5:/tx_sens0"
"phantom.h5:/tx_sens1"
whereas the transceive phase data would come from
"phantom.h5:/trx_phase00" "phantom.h5:/trx_phase10"
"phantom.h5:/trx_phase01" "phantom.h5:/trx_phase11"
"phantom.h5:/trx_phase02" "phantom.h5:/trx_phase12"
"phantom.h5:/trx_phase03" "phantom.h5:/trx_phase13"
Wildcard characters
It is possible to change the default wildcard characters, the starting index and the increasing step with the following optional instructions in the .toml configuration file.
[input.wildcard]
tx-character = '>'
rx-character = '<'
start-from = 0
step = 1
Output
[output]
electric-conductivity = "example.h5:/sigma" # [S/m]
relative-permittivity = "example.h5:/epsr"
electric-conductivityis the address where the electric conductivity, expressed in siemens per meter, will be written. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file.relative-permittivityis the address where the relative permittivity will be written. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file.
If an output address is not provided in the configuration file, the corresponding properties evaluation will not be stored.
Postprocessing
The following set of instruction is optional. It can be used to apply a filter in postprocessing to the EPT results.
[postprocessing]
output-electric-conductivity = "example.h5:/sigma-postpro"
output-relative-permittivity = "example.h5:/epsr-postpro"
perform-only-postprocessing = false
input-electric-conductivity = ""
input-relative-permittivity = ""
input-reference-image = ""
input-electric-conductivity-variance-map = ""
input-relative-permittivity-variance-map = ""
kernel-size = [5, 5, 5]
kernel-shape = 1
weight-param = 0.10
output-electric-conductivityis the address where the postprocessed electric conductivity, expressed in siemens per meter, will be written. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. If it is an empty string, the postprocessing will not be applied to the electric conductivity map (default: empty string).output-relative-permittivityis the address where the postprocessed relative permittivity will be written. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. If it is an empty string, the postprocessing will not be applied to the relative permittivity map (default: empty string).perform-only-postprocessingis equal tofalseif the postprocessing must be applied to the result of the EPT method. It is equal totrueif only the postprocessing must be performed in a provided set of input maps (default:false).input-electric-conductivityis the address of the electric conductivity map to be filtered. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. It is used only ifperform-only-postprocessingistrue, otherwise the electric conductivity computed by the EPT method is used as input (default: empty string).input-relative-permittivityis the address of the relative permittivity map to be filtered. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. It is used only ifperform-only-postprocessingistrue, otherwise the relative permittivity computed by the EPT method is used as input (default: empty string).input-reference-imageis the address of the reference image used by the filter. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. It is used only ifperform-only-postprocessingistrue, otherwise the reference image provided to the EPT method is used as input, when available (default: empty string).input-electric-conductivity-variance-mapis the address of the electric conductivity variance map used by the filter. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. It is used only ifperform-only-postprocessingistrue, otherwise the variance map estimated by the EPT method is used as input, when available (default: empty string).input-relative-permittivity-variance-mapis the address of the relative permittivity variance map used by the filter. It must be a dataset in an .h5 file. It is used only ifperform-only-postprocessingistrue, otherwise the variance map estimated by the EPT method is used as input, when available (default: empty string).kernel-sizeis the number of voxels along each semi-axis of the filter kernel (default:[1,1,1]).kernel-shapeselects the kernel shape according to the following table (default:2).weight-paramis a parameter of the weight function used for the reference image (default:0.10).
| Code | Shape | Example with size = [2,2,1] |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Cross | 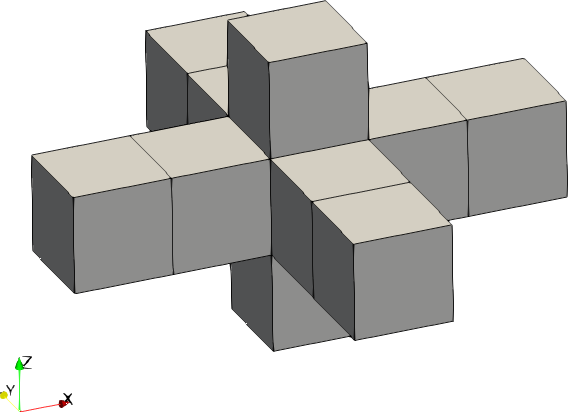 |
| 1 | Ellipsoid | 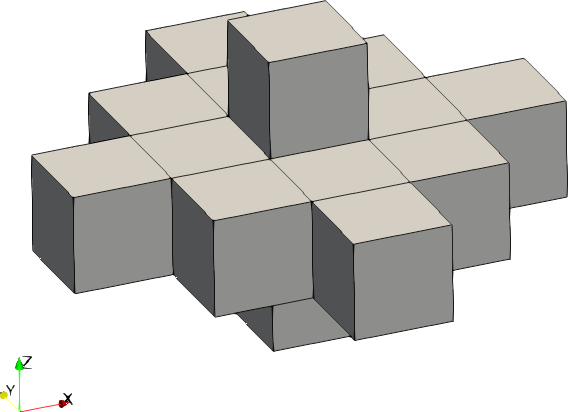 |
| 2 | Cuboid | 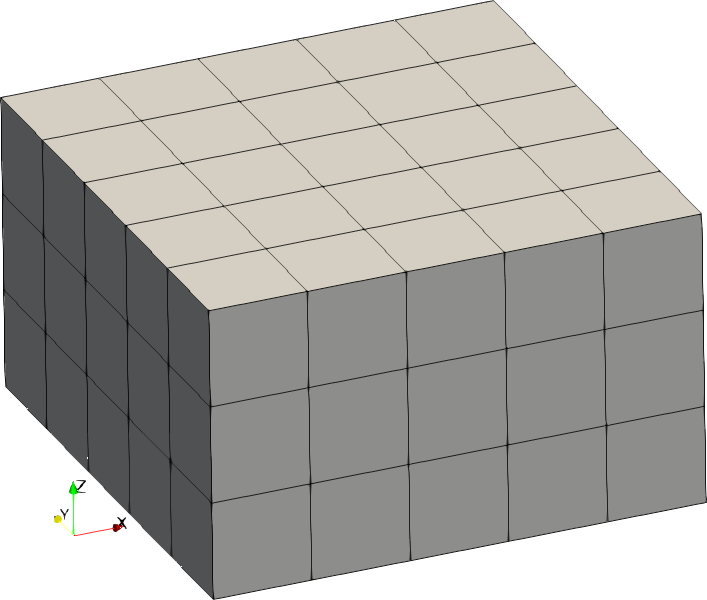 |
The postprocessing filter is selected according to the following decision tree:
- If neither the reference image nor the variance map are available, a median filter is applied.
- If the reference image is available, but the variance map is not, a median filter whose kernel is anatomically adapted is applied.
- If the reference image is not available, but the variance map is, a moving weighted average is applied, using the reciprocal of the variance map values as weight.
- If both the reference image and the variance map are available, a moving weighted average whose kernel is anatomically adapted is applied, using the reciprocal of the variance map values as weight.
The filter kernel is anatomically adapted with respect to the reference image according to a hard threshold rule: only the voxels whose relative contrast with respect to the central voxel is lower than weight-param are kept in the kernel.
Parameters
In addition to the previous settings, that are common to all EPT methods, each method could require some additional parameters. The settings for each specific EPT method are described in their pages, where examples of configuration files are also provided (see Methods).